Paper marketing materials provide a way for individual stores to deliver messaging about their products and promotions to each prospect within the point of sale’s marketing zone. This local distribution method is important because it focuses on a predefined geographical area to identify all potential consumers around its point of sale.
However, several factors can influence this traditional communication channel, including:
- Paper printing costs which weigh heavily on advertisers’ marketing budgets, especially given the nearly 15% rise in the cost of wood, paper, and cardboard that took place over the past year and is likely to continue
- New environmental regulations like the “Oui-Pub” initiative aimed at restricting the distribution of non-consensual marketing materials to mailboxes
In light of these new challenges, it’s important for advertisers to begin integrating innovative communication channels that complement their paper marketing campaigns. Digitizing business operations allows companies to capture the reach achieved by paper marketing campaigns and further optimize it.
Since you’re here ! Check out our: Guide : Transitioning to digital circulars
A dynamic catchment area
As previously discussed, advertisers use geographic location as a basis for distributing their paper materials. They determine a marketing zone that allows them to identify households that are likely to shop in their stores based on proximity.
It’s essential to continue with this aspect when digitizing communications, because although technology allows advertisers to refine their marketing zones using algorithms, it identifies users who are already familiar with or loyal to the brand.
By adding a dynamic, smart dimension to this basis, transitioning to digital advertising provides an opportunity for companies to optimize their consumer pool while continuing to address their original target audiences. To do this, it’s important to analyze user-consented geographical data which makes it possible to determine where mobile device users work, live, and spend their time. For example, users who live outside of a store’s marketing zone but walk by it every day on their way to work should be included in the store’s target audience.
Using geolocation data allows marketers to identify numerous new prospects that extend beyond their original geographic marketing zone. While they may not live in the zone, they frequent the area on a regular or even daily basis. This is why dynamic marketing zones are so important.
How to Ensure the Accuracy of This Strategy

To optimize the reach of paper marketing campaigns, data quality and reliability are crucial.
When collecting data, to best determine the geographical context of each mobile user, it’s essential to remove any that appears to be inconsistent. These data points are called “outliers.” User-consented mobile device data is used to define target audiences. Geographic data makes up a large portion of the data collected by devices. This large quantity of data can then be analyzed to remove any geolocation outliers, data points that are remote or illogical when compared to others.
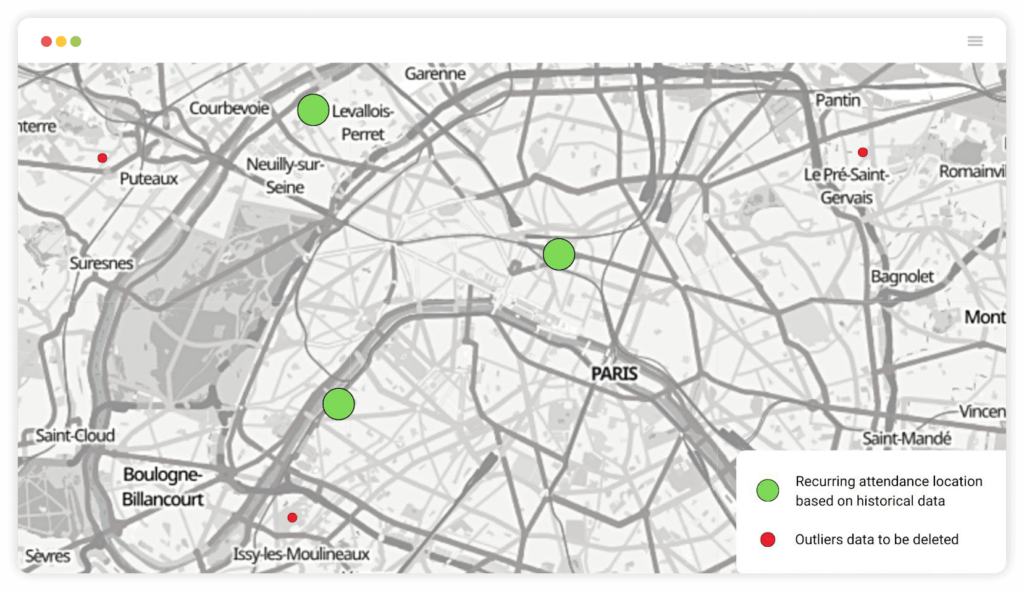
This data also provides an opportunity to determine uninhabitable areas within a marketing zone or potential “obstacles” (golf courses, the ocean, or a competitor’s marketing zone).
Thanks to machine learning, it is now possible to create reliable dynamic marketing zones. These zones allow you to optimize the reach of each message, whether you’re marketing to audiences living near your point of sale or those likely to be passing through.





